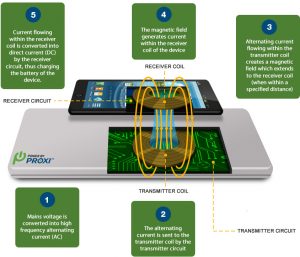
But the concept brings with it a division of ideas, with some arguing that it provides a number of efficiency, cost and safety advantages over the traditional charging cable; and others worrying about the harmful effects that may come with having power all around you. Firstly, let’s get to know how wireless smartphone charging works. It uses a resonant inductive coupling between the sender (the charging station) and the receiver (the smartphone). You will need to feed power to the charging station which contains a transmitter coil. An electromagnetic field forms around the transmitter and once the receiver coil comes near enough, it interacts with the magnetic field to create an electric current. By putting the second coil inside another device, you can wirelessly transfer power from the charging station to the device. So, is it safe for the battery? Yes and No. The electromagnetic fields generated by the transmitters are very small and weak in power, a convenience for consumers. This also enables safe charging in a hazardous environment where an electrical spark could cause an explosion. However, a wireless charger can get quite warm during charging as lost energy is turned into heat. This causes stress on the device’s battery as it sits on the mat, an issue that could result into wearing out of the battery. The electromagnetic radiation is limited to the immediate area of the wireless charging station, only when a device is charging. With a power limit of 5 watts for the inductive charging, the worries are less.
The significant disadvantage, though, is using the device while it is charging. With wired charging, you can move here and there with your device in the hand; but wireless charging does not accord you any of that. You have to place the device on a charging mat for it to fully charge, otherwise it will not.